Modeler: Tutorial/Subtype and Generalisation
Classification and Qualification of subtypes
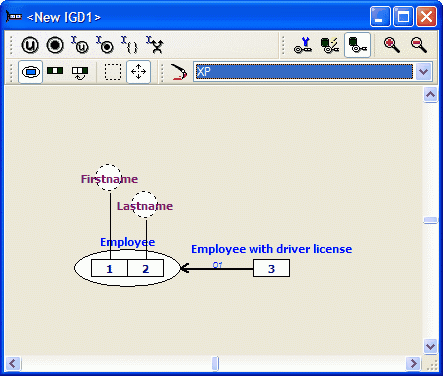
The classification and qualification of subtypes is identical to the classification and qualification of other fact type expressions. The classification and the qualification of the example below automatically generates a subtype structure. ('Employee with Driving Licence' as subtype of 'Employee').
CaseTalk marks fact types containing one role played by an nominalized fact type automatically as a subtype.
Creating subtypes after classification and qualification
Execute the steps below to create a subtype in an existing information grammar:
1. Select the supertype in the IG Viewer.
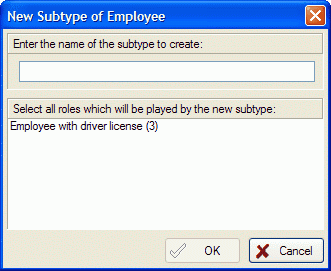
2. Select New Subtype from it's popup-menu:
3. Enter the name of the subtype and select the fact types you like to transfer to the subtype.
4. Click Ok.
Classification and qualification of common subtypes
Execute the steps below to create a common subtype:
1. Enter a fact type expression containing all roles of the common subtype. (For example: 'The bike NT-15-RT is the motorcycle NT-15-RT' for the common subtype Motorbike).
2. Add population to common subtype using the population editor and the fact type expression from step 1.
3. Add other object or fact type expressions to the common subtype. Make sure the labels in these expressions have already be added to the common subtype during step 1 or 2.
4. Add the unicity constraints after you have added all fact type expressions and population.
Classification and qualification of generalizations
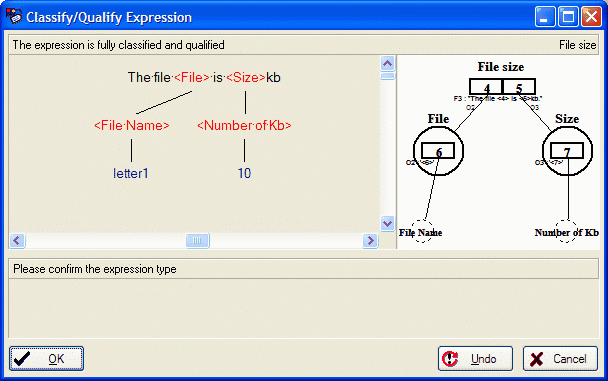
The classification and qualification of generalizations is identical to the classification and qualification of other fact type expressions. The classification and the qualification of the example below automatically generates a generalized structure:
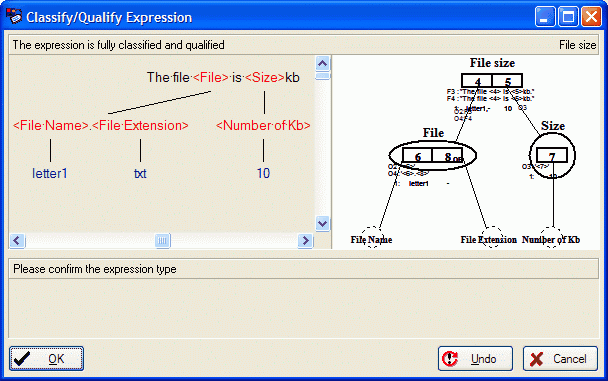
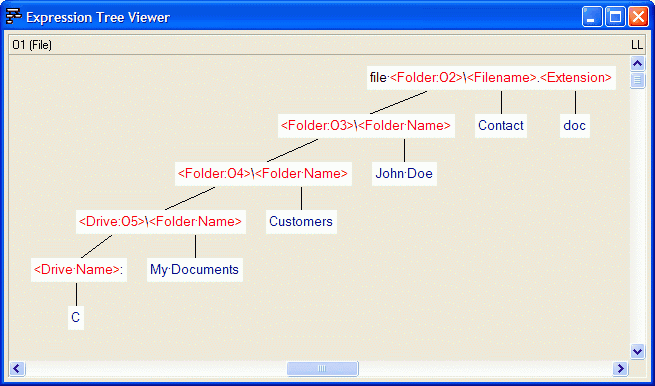
The casetool tries to match the fact expression below with 'file is Kb'. But this match is not correct. After we have clicked the Try OTL button, the casetool tried to match the fact expression on the OTL level. This match is ok: ' is '. When matching the object expression 'file letter2.txt' we have a similar situation. First you should click Try OTL then you should click No Match:
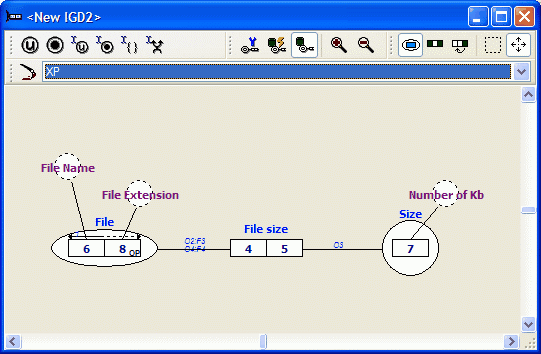
The diagram (after placing a few UC's) may look like this, the 'OP'-tional role is visible:
The UC arrow is partially dotted because of this optional role.
Classification and qualification of recursive structures
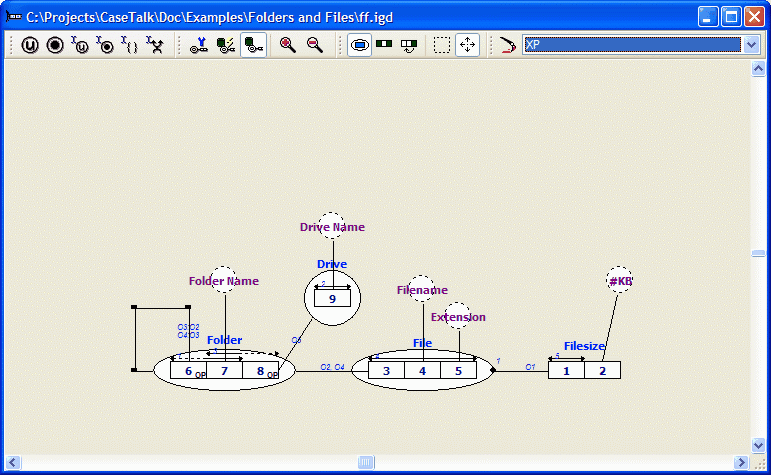
The classification and qualification of generalizations is identical to the classification and qualification of other fact type expressions. The classification and the qualification of the example below automatically generates a recursive (and generalized) structure:
The diagram looks like this:
Back: Using the plugin modules
Next: Integrity Checks