Modeler: Tutorial/Deriving a Database Schema
In this lesson you will learn how to check the integrity of an information grammar and how to derive a database schema.
Checking the integrity of an information grammar
Preparation
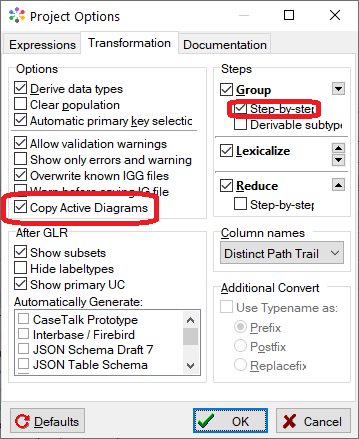
1. Open the Run menu and select Settings.
2. Check Copy Active Diagrams and Step by Step and make sure the other settings are as shown below:
3. Click OK.
Note: Some CaseTalk versions didn't pick up the settings until restarted and the project is reopened.
Verify well-formedness
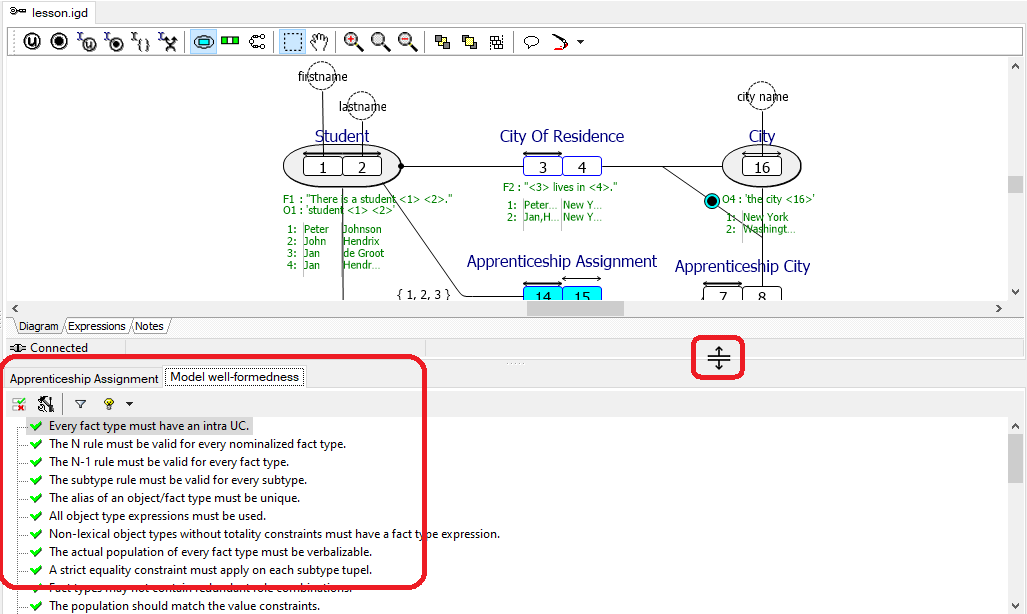
1. Click menu Run, Verify well-formednes.. Casetalk automatically performs a model Integrity Check. If the casetool encounters any errors the Integrity Check window will be opened so you can examine the error. If Integrity Check encounters only warnings, the Integrity Check window will not be opened.
2. After the Integrity Check, the result is visible below the diagram. You can change the window-size for a better view.
A detailed description of the checks can be found in appendix B.
Step-by-step grouping
Step by step grouping is hardly used in daily practice because of the large number of roles that are present in most models. The following steps are only for the purpose of education and understanding the grouping process using a small model.
1. Open the Run menu and select Transform
2. Casetalk automatically transforms the model. After a while, this window appears:
3. Click yes.
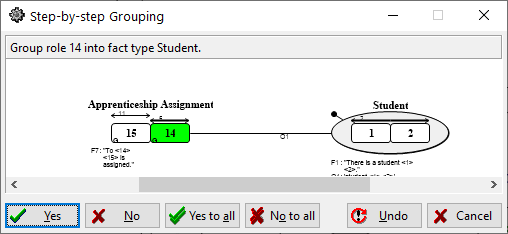
4. CaseTalk now shows this window:
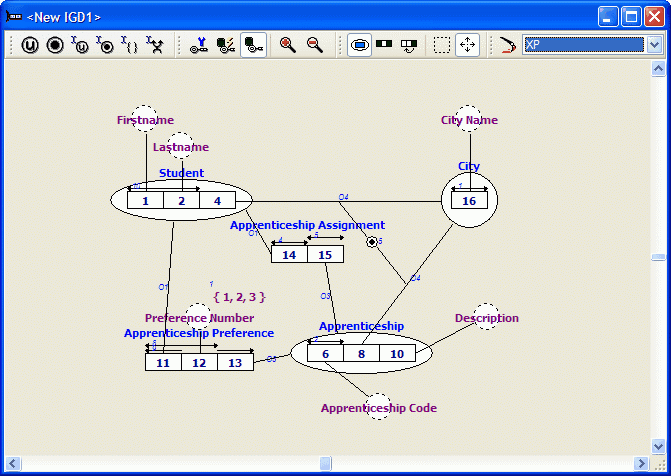
Since there are two separate UC’s on role 14 and 15, CaseTalk has to decide how to group these roles, and it proposes to group role 14 into the fact type Student.
5. Click Yes.
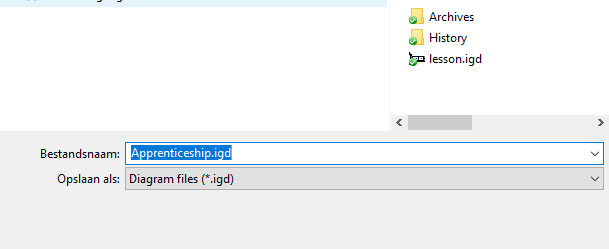
Casetalk shows the next proposal. You can click Yes for each separate proposals, or click Yes to all to approve all following proposals. 6. Casetalk now shows a window to save your transformed model:
7. Save the transformed diagram as Apprenticeship.igd.
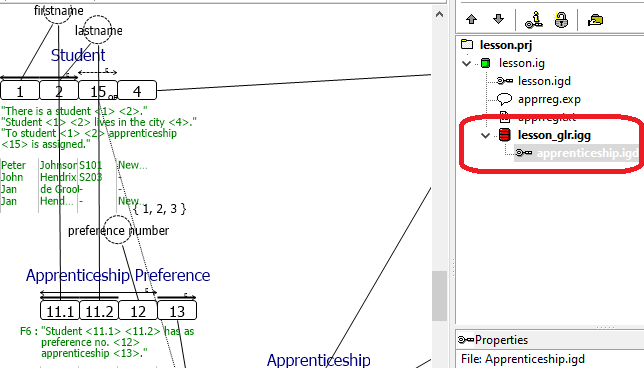
The project manager on the right now shows the grouped grammar and diagram:
For the purpose of this tutorial, we’re going to rerun the transformation with other settings, so delete the two files that you’ve just created:
8. Rightclick on lesson_glr.igg and choose Remove from project. Confirm with Yes and notice that the grouped diagram is also deleted.
Note: if the repository-window on the left has suddenly disappeared, double click on the green IG-icon on the projectmanager:
9. Save the project by selecting Save All from the File menu.
Setting grouping marks before grouping
Step 19
1. Open the diagram.
2. Click on 'Assigned Apprenticeship' in the Repository window.
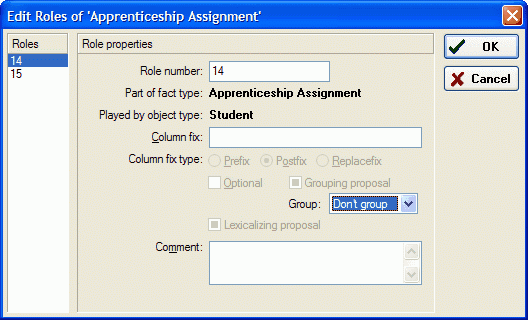
3. Select Edit Roles from it's popup-menu:
4. Select role 14 and set the grouping to 'Do not group'.
5. Repeat this for role 15.
By unchecking roles 14 and 15 you have indicated you do not want to group these roles.
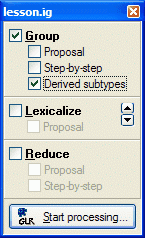
6. Open the Tasks menu and select GLR:
Make sure all options are set as displayed above.
Note: Do not check Step-by-step grouping. The Step-by-step grouping algorithm ignores the User Override property.
7. Click Start processing.
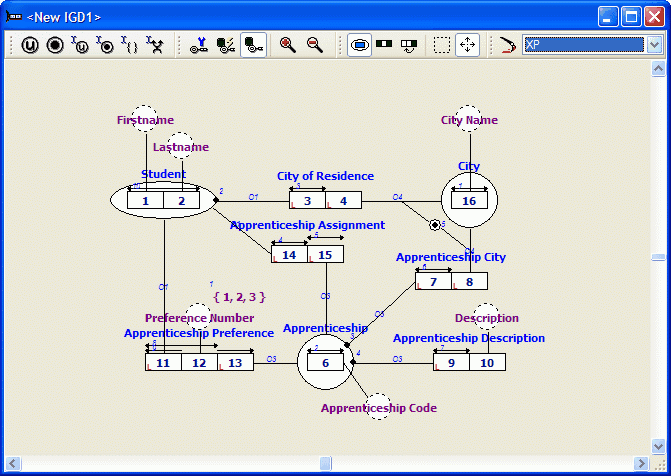
The generated information grammar is not in Optimal Normal Form (ONF). This structure might be choosen if 'Assigned Apprenticeship' is unknown for most of the students. (Grouping 'Assigned Apprenticeship' then results in a Student table with too many NULL values in the Assigned Apprenticeship column).
Deriving a lexicalizing proposal
1. Select the GLR window:
And select only the lexicalize and proposal option.
2. Click Start...
All roles which should be lexicalized will be marked with a 'L' in the diagram:
3. Close the project by selecting Close Project from the File menu. Do not save the project.
Lexicalizing
To show all options of the lexicalizing and reducing algorithm we will use a slightly different information grammar in the following exercises.
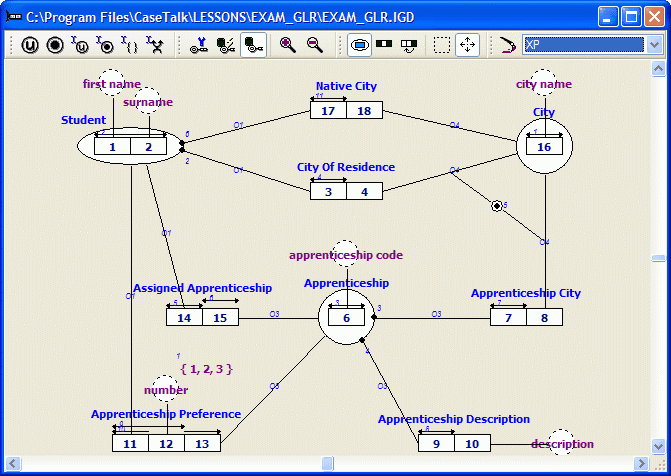
A fact type expression has been added to 'City'. Without this fact type expression City would have been removed during the lexicalizing process. Now it will be reduced during the reducing process.
A new fact type (Native City) has been added to 'Student'. By adding this fact type we have created a column naming conflict in the 'Student' table.
1. Open the File menu and select Open Project. Open the 'EXAM_GLR' project from the '...\LESSONS\EXAM_GLR' directory.
2. Open the Tasks menu and select GLR:
Make sure all options are set as displayed above.
3. Click Start...
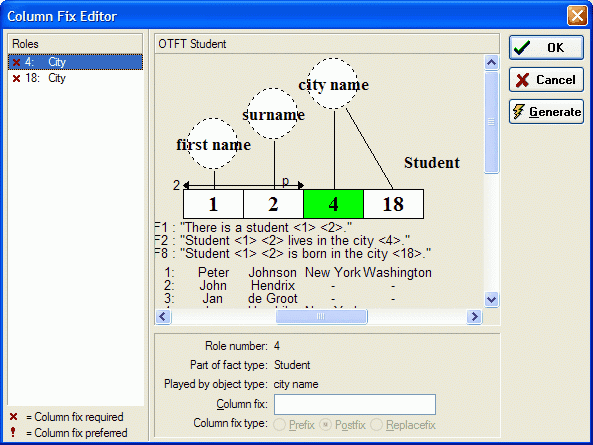
Roles 4 and 18 are both played by 'city name'. To prevent a column naming conflict this Column Fix Editor is shown.
By clicking the Generate button the casetool will automatically add numbers behind the column names.
4. Select role 4 and enter the prefix 'Residence'. (Don't forget to set the Column Fix Type.)
5. Select role 18 and enter the prefix 'Native', then click Ok.
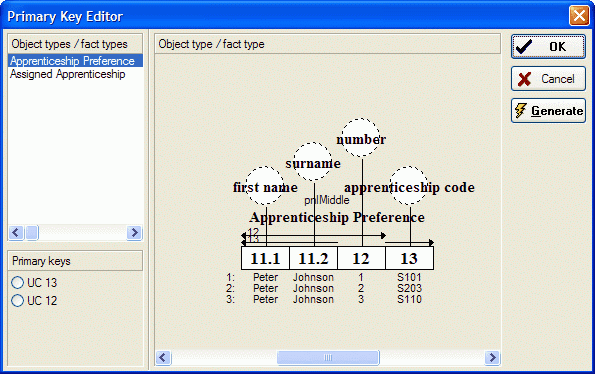
In the appearing Primary Key Editor you can select which uniqueness constraint should be taken as primary keys. (If there are fact types with multiple uniqueness constraints).
In the left section a list of fact types with multiple uniqueness constraints is displayed. Below this list you will find a the list with the uniqueness constaints of the selected fact type. Each of the uniqueness constraints in this list can be checked. In the right section the selected fact type is displayed.
6. Choose UC14 for 'Assigned Apprenticeship'.
7. Select 'Apprenticeship Preference'.
8. Choose UC12 for 'Apprenticeship Preference'.
9. After you've completed this lesson, please select the menu 'File\Close All' and than select 'File\Reopen\AppReg\Lesson.prj'.
Deriving a reduction proposal
1.Select the GLR window:
Make sure the options are set as displayed above.
2.Click Start...
The object type 'City' will be marked for reduction with an (R) behind the object type name.
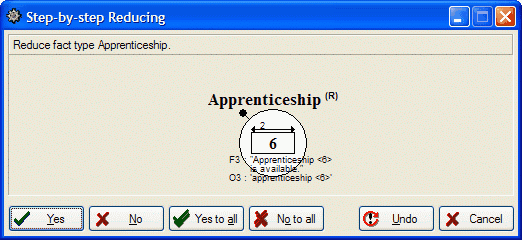
Reducing
1. Select the GLR window:
Make sure the options are set as displayed above.
2. Click Start...
3. Click Yes to reduce everything.
4. Open the File menu and select Close Project. Do not save the project.
Generating Table Documentation
Step 19
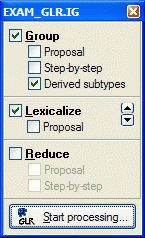
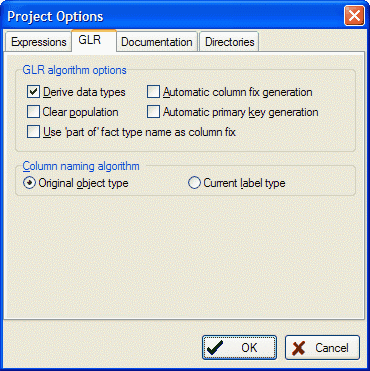
1. Open the Options menu and select Project, than activate the GLR tab:
2. Check the options Automatic Column Fix Generation and Automatic Primary Key Generation, then click Ok. Read the information box below for more information about the GLR options.
GLR Options:
Derive data types: If this options is selected the casetool will derive a datatype proposal during the GLR process. The casetool will generate Char and Numeric datatypes. If you have entered other datatypes they will not be affected by this option. If you have used Char and Numeric yourself and the casetool has detected labels exceeding the total and/or decimal length you have specified these attributes will be updated.
Clear Population: If this option is selected, all population will be removed during the GLR process.
Automatic Column Fix Generation: If this option is selected and column naming conflicts are discovered, conflicting columns will be made unique by adding a number as postfix.
Automatic Primary Key Generation: If this option is selected and fact types with multiple primary keys are discovered, this algorithm will choose the first uniqueness constraint not covering optional roles. If all uniqueness constraints cover optional roles (only for generalisations) then all uniqueness constraints will be made primary.
3. Open the Tasks menu and select GLR:
Make sure all options are set as displayed above.
4. Click Start...
The information grammar will now be grouped, lexicalized and reduced.
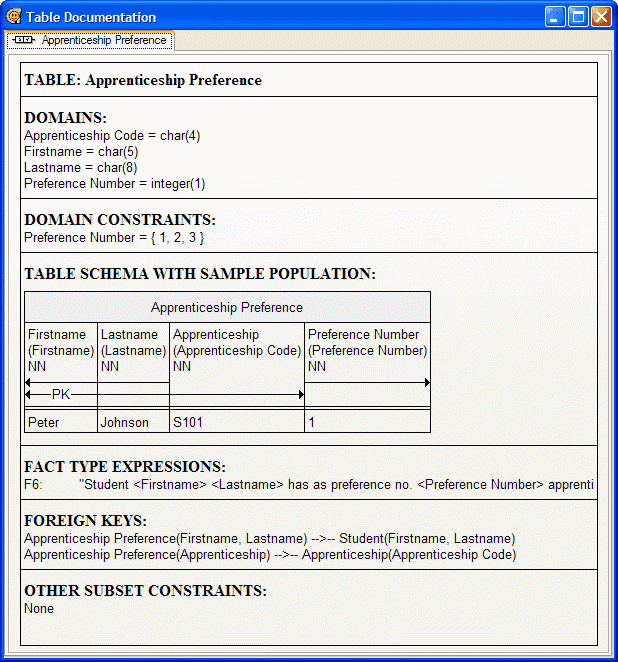
5. Click on 'Apprenticeship Preference' in the Repository.
6. Open the View menu and select Table Documentation:
A window will appear containing the table documentation for 'Apprenticeship Preference':
7. Keep the Table Documentation window open and select another fact type from the Repository window.
Note: The contents of the Table Documentation window will change automatically.
8. Close the Table Documentation window.
9. Open the File menu and select Save Project. If necessary save the diagram as 'lesson2.igd'.
You can print the table documentation by selection Print or Print All from it's the popup-menu.
Back: Constraints
Next: Using the plugin modules